ISO 14971 RISK MANAGEMENT FOR MEDICAL DEVICES
Let’s review the background of ISO 14971. As a medical device manufacturer, the first thing you need to do is to make sure that your devices do what they are supposed to do. Then, you need to make sure that they meet the set regulations and standards for the markets you intend for them to be used.
Risk management is an integral part of the manufacture and eventual sale and acceptance of medical devices in the market. When manufacturing medical devices, manufacturers should always consider that the end-user may not have a choice on the device to use.
Therefore, as a manufacturer, you should meet all the laid-out risk management standards for your devices to be accepted by regulators and doctors who use them on their customers.
What Is Risk Management ?
Risk management is the process through which a medical device manufacturer can identify and analyze hazards and risks and develop policies to control and monitor the risks.
Risk is the probability of occurrence of harm and the extent of the harm if it does occur.
ISO 14971
ISO 14971 is the current International Standard that provides instructions and guidelines for risk management of medical device manufacturing.
The standard should be used to guide medical device manufacturers in coming up with and following a proper risk management process.
Regulators follow the guidelines provided by this standard in evaluating and allowing medical devices into the market.
ISO 14971 was developed to provide a standardized process of identifying and monitoring risk across the lifecycle of a medical device. This standard ensures that these risks are monitored from the product design and conception stage, procurement, production, and post-market use.
Medical devices attract interest from diverse stakeholders. These include manufacturers, doctors, governments, other healthcare practitioners, and patients. Thus a standard framework on the risk management processes for medical devices is important to bring all these stakeholders to agree on the risk management process of the devices.
In addition to the guidelines provided in the standard are annexes to the document. Contained in the annexes are in-depth explanations of the guidelines and detailed examples of how to implement the risk management procedures provided.
This standard has evolved over time to become a comprehensive guide on risk management for medical devices manufacturers. The current state-of-the-art guide was recently republished in 2019. Previous standards are now used as guides to the current standard.
ISO 14971 contains definitions of terms that relate to medical device risk management. It also gives some general requirements for a risk management system, It then goes ahead to provide guides on risk analysis, evaluation, and control. It also provides a risk management review guide and production and post-production activities for medical devices.
Some terms defined in the ISO 14971 include:
Hazard-a source of possible harm.
Harm- a physical injury on a person or damage to property or environment.
Risk analysis- the process of identifying hazards and calculating the severity of harm with available information.
Risk estimation- the process of calculating the probability of harm occurring and estimating its severity.
Risk evaluation-connecting risk severity to risk criteria
Risk control-process of coming up with measures to eliminate, reduce or maintain risk at a certain level.
Residual risk- the risk that may occur even after you have taken the necessary risk control measures.
Risk Management Process
When you have studied and understood the ISO 14971 standard, it is now for you to build your risk management process. To begin the development of the risk management process for a medical device manufacturer, the top management of the organization is involved.
The ISO 14971 recommends that top management be responsible for and provide resources for comprehensive risk management. The top management is also required to produce a risk management policy that sets acceptable risk levels for the devices they produce.
The risk management process as provided for by ISO 14971 involves the following steps.
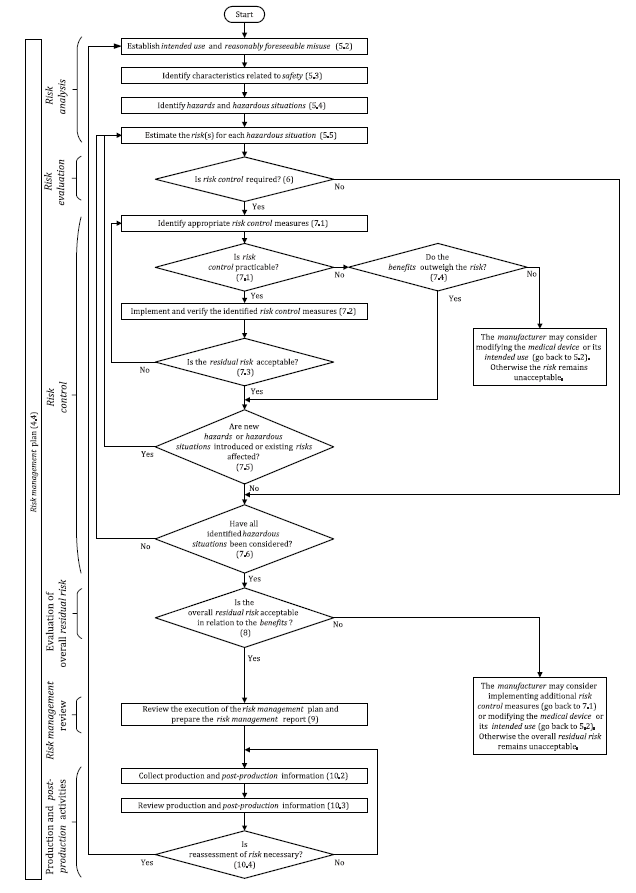
Step 1. The creation of a risk management framework in the organization
The top management of the organization is required to create a written policy of the organization’s risk management plan for all the medical devices they manufacture. This will help to come up with a clear risk management process that includes the roles and responsibilities of the different parties in the organization.
Step 2. Identify and provide the intended use of the device being manufactured
The risk management policy must identify the device for which the risk management process is being made. It should also state the intended use of the device once it is on the market.
This helps to easily assess the risks that may be associated with the device in its lifecycle.
Step 3. Identify Hazards
The top management together with the design / production team should identify potential sources of risk for the device they are designing / manufacturing at this stage of developing the risk management process.
Step 4. Identify any foreseeable misuse
This helps to identify potential risks and plan ahead on how to avoid them.
Step 5. Risk estimation
Evaluate the severity of potential risk if it ever occurred.
Step 6. Risk evaluation
With potential risks identified, how likely are they to occur? Is it possible to reduce the frequency with which the risks are likely to occur?
Answer these two questions at this stage.
Step 7. Risk Control
The organization needs to prepare risk controls for when risks occur. Risk control involves steps or conditions that can limit the severity of the risk if it occurs.
Step 8. Evaluate Risk Acceptability
Considering the intent of the medical device you are manufacturing, are the risks identified acceptable? If they are, are there ways to minimize the likelihood of the risk occurring and its severity?
Answers to these questions will allow you to keep producing the device if the impact of its use is positive.
If you evaluated the risk acceptability level and found it unacceptable, then you can discontinue the production of the medical device.
Step 9. Review Your Risk Management Process
Review the risk management process by checking that you have followed the organizational policy on risk management. Also, it is best to refer to the ISO guide to ensure that you have followed the right process. Then prepare a report on your review.
You can now start the production of your device.
Step 10. Production And Post Production Activities
Record and report any new information that arises from the production of the device. If you will carry out tests, record all the new information you may get. Record customer feedback on how the product works and any likelihood of previously unidentified risks.
Risk management and review is a continuous process. Hence the need to look for and record any new information on the manufactured device.
Make A Risk Management Plan
At the top management level, the organization will develop the policy around the risk management process. Ideally, this should happen before your product goes into production. It should also be reviewed as new information arises post-production.
When you have your product in the market, you need to make a risk management plan. This is a plan for how to deal with risks that arise now that the product is on the market.
Normally, if you only produce one product, the risk management process is sufficient for a risk management plan. If you have multiple products, you need a risk management plan for each product.
With your risk management process as a guide, list all the risks identified that could affect your product. Then list all the action steps you will take to control or minimize the risk if it occurs.
Record any activities that will take place and identify those who will be responsible for the different risk management activities. Have a risk management team for every medical device you bring to the market. They should be well versed with the manufacturing and purpose of the product.
In the risk management plan, identify how you will capture new information that will assist in risk management.
Keep revising the risk management plan when you have any new information regarding the likelihood of an identified risk occurring or not.
Investigate The Risk
When you have a product-specific risk management plan in place, the next step is investigating the risk. Consider the intended use of the product and the foreseeable misuse. Using these parameters, you could easily come up with hazards that would cause potential risks to your product. A risk analysis tool will help you to do this.
The first step is investigating risks that could arise around the value chain of your product and service. Identify risks from and on parties such as your suppliers, risks that may arise when shipping the product to the directions market among other types of risks.
There are lots of tools available that you can use for risk analysis.
Once you have identified the risks that your product would arise, you now need to come up with ways to control your risk. In this case, you could set rules around the use of the product so that you could easily manage the risks.
Carrying out user training so that that the users will use the product as it is intended for. You could also use warning labels stuck on the device to show how it is intended to be used. Doctors and other users can follow these warnings to ensure that the device is used in the right way.
Also, carry out a risk-benefit analysis. This will help you to identify whether the risks are greater than the benefits that will be gained from the use of the medical device you are creating. This you will do over the lifecycle of the device you are creating.
Risk Controls
Risk controls are the measures you take with your device to reduce the impact and likelihood of occurrence of identified risks.
Risk controls are part of the risk management process. When developing a policy on how to handle risks, you need to think about lowering the chances of the risk occurring.
Risk controls can be considered at different levels of the lifecycle of the medical device you are manufacturing. The first level is at the design and production of the medical device. At this point, manufacturing entities should seek to add inherent safety features that may reduce the occurrence of risks.
This means that the device should be designed in such a way that it is already safe by the time it gets to trial in the market.
The other level of risk control to consider is ensuring that there are protective measures within the device. If one of the risks identified is electrical problems, manufacturers can add a fuse that limits the usage of the power by the product. This will reduce the risk of an electrical fault caused by the device or damaging the device.
The third level of risk controls is in providing warnings and instructions for use on the device. This level considers the purpose for which the device was manufactured. It also considers the possibility of misuse.
Thus, the manufacturer can provide instructions for use on the device. If it is a large enough device, the instructions can be stuck on the device. For a small device, the instructions can be written on the packaging.
Additionally, manufacturers can organize training for the main users of the medical devices to ensure that they use the devices as is required. It also helps to make sure that risks are also controlled for the user.
Create A Report From Your Risk Management Outcomes
When you have comprehensively followed the ISO 14971 guidelines on the risk management process of your device, you will need to document everything you have done.
You will do this by creating a risk management report for your device or devices. In this report, you will confirm that you followed all the ISO standard for medical device risk management. You will also document the results of your risk management mitigation and how you reduced inherent risk on the medical device you produce.
Last, ISO 14971 has strong connection with other standards. First of all ISO 13485 because this standard has numerous references to risk management and therefore ISO 14971 methods should be implemented. Other standards have also strong links with ISO 14971. To name a few: ISO 10993-1 (biological evaluation of medical devices), IEC 62344 (medical device software) or IEC 62366-1 (usability).








